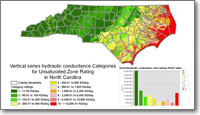
| Brunswick County Groundwater-Level Monitoring |
 |
Since 2000, the population of Brunswick County has grown by more than 50%, over two times the 22% growth experienced by the State of North Carolina as a whole (U.S. Census Bureau, 2014). A growth of this magnitude places significant stress on Brunswick County's natural resources. County planners have recognized the potential consequences of land use changes associated with growth and the resulting increased demand on water resources by consolidating the many public utility providers into one organization and embarking on an aggressive utility expansion plan. In order to make informed water resource planning decisions, County officials need up-to-date water-resource information. To address concerns about the availability of groundwater in the Brunswick County area, the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) and Brunswick County initiated a cooperative water-resources program in 1998.
Science Topic:
Increased Population and Water Resources
Groundwater resources
Hydrologic and Geospatial data
|
| Catawba-Wateree Groundwater Network |
 |
The recent multiyear drought in North and South Carolina (summer 1998-fall 2002) made critical the recognition of the vulnerability of the water resources in these two States to climatic conditions. To prepare for drought conditions in the future, water managers and State and Federal water-resource agencies are seeking tools to assess hydrologic conditions in both a predictive and responsive manner. Monitoring networks of near real-time streamflow gages (surface-water stage/discharge) and wells (groundwater levels) are essential components typically used to assess hydrologic conditions.
Science Topic:
Groundwater resources
Hydrologic and Geospatial data
|
| Charlotte/Mecklenburg Hydrologic Network |
 |
The Charlotte-Mecklenburg Hydrologic Network installed its first raingage in 1989, and has grown to 72 raingages and 54 streamgages. Originally the network used landline telemetry for data retrieval but has been upgraded to transmit data using ultrahigh frequency (UHF) radios and satellite telemetry.
Science Topic:
Hydrologic Hazards
Hydrologic and Geospatial data
|
| National Trends Network (Precipitation) - Station NC36 |
 |
The National Atmospheric Deposition Program/National Trends Network (NADP/NTN) is a nationwide network of over 250 precipitation monitoring sites. The network is a cooperative effort between many different groups, including the U.S. Geological Survey, who has operated the Jordan Creek Station (NC36) in Scotland County, North Carolina since 1983.
Science Topic:
Support of Federal and State Programs
Hydrologic and Geospatial data
|
| Roanoke River Water-Quality Monitoring and Modeling |
 |
The relations among river flow, floodplain water level, and instream dissolved-oxygen (DO) concentrations are important but poorly understood for the Roanoke River. Flooding and floodplain inundation no longer follow a natural seasonal pattern of flooding in the winter and occasionally in the fall, and lower flows throughout the remainder of the year, but are primarily governed by upstream reservoir releases. The timing, duration, and extent of floodplain inundation can have either positive or negative effects on the ecosystem in the lower Roanoke River corridor, depending on the inundation characteristics. Timing, depth, and duration of floodplain inundation affects habitat use and reproductive success of wildlife and regeneration of bottomland hardwood trees.
Science Topic:
Estuarine and Coastal Processes
Support of Federal and State Programs
Hydrologic and Geospatial data
|
| Effects of land-use change on water-quality in the Treyburn Development of the Falls Lake Watershed |
 |
Since 1988, the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) has been collecting data at 18 sites in and around Treyburn, North Carolina, which is an 8-square-mile (mi2) residential, commercial, and industrial development located in the Falls Lake watershed. Water-quality data, assessments of biological conditions, and streamflow information have been collected at the sites over different time intervals. No single stream drains the entire Treyburn development.
Science Topic:
Increased Population and Water Resources
Hydrologic and Geospatial data
|
| Triangle Area Water Supply Monitoring |
 |
The Research Triangle area, located within the upper Cape Fear and Neuse River basins, is one of the most rapidly developing areas of North Carolina. Growth has increased demand for water from public suppliers, the majority of which draw water from streams and lakes in the region. Growth also brings the threat of greater loads of contaminants and new contaminant sources that, if not properly managed, could adversely affect water quality.
Science Topic:
Increased Population and Water Resources
Hydrologic and Geospatial data
|
| Pee Dee National Wildlife Refuge flow model |
 |
The U.S. Geological Survey and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service entered into a cooperative agreement to develop a model of streamflow and inundation in the Pee Dee National Wildlife Refuge area. The resulting flow model will be used to better understand streamflow and flooding in the area and serve to protect refuge assets and sensitive habitat areas.
Science Topic:
Hydrologic and Geospatial data
Hydrologic Hazards
|
| Continuous water-quality monitoring at Lake Mattamuskeet |
 |
The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service has partnered with the U.S. Geological Survey to establish two automated continuous water-quality monitoring stations at Lake Mattamuskeet to collect data useful for management of the lake. Stations on the east and west side of the lake measure water level, clarity, dissolved oxygen, pH, temperature, salinity, and conductivity.
Science Topic:
Hydrologic and Geospatial data
Support of Federal and State Programs
Aquatic Habitat Restoration
|